
Write something
DeepSeek’s engram
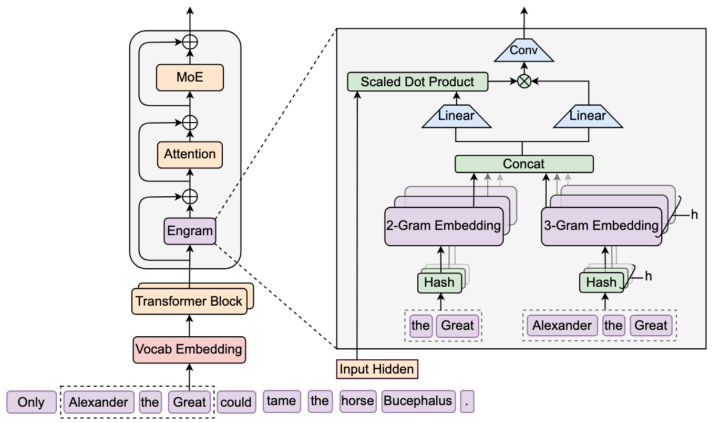
I missed this one, with all my focus on context management tech and the whole stochasticity (a word I struggle to pronounce, much less type) of inference. But it is January, which means the folks at DeepSeek have made more key architecture improvements. I’ll just let them tell you (and why is their English so much better than so many native speakers). I‘ll be honest, it’s going to take me a couple days to make sense of this, but my analysis will eventually be in the Burstiness and Perplexity Skool group (bleeding edge classroom): “While Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) scales capacity via conditional computation, Transformers lack a native primitive for knowledge lookup, forcing them to inefficiently simulate retrieval through computation. To address this, we introduce conditional memory as a complementary sparsity axis, instantiated via Engram, a module that modernizes classic 𝑁-gram embedding for O(1) lookup. By formulating the Sparsity Allocation problem, we uncover a U-shaped scaling law that optimizes the trade-off between neural computation (MoE) and static memory (Engram).” #deepseek #engram #aiarchitecture #hiddenstatedriftmastermind
1
0
DeepSeek’s Public Return: AI Disruption Warning Signals Strategic Shift in China’s Tech Narrative
DeepSeek senior researcher Chen Deli delivered a stark warning about artificial intelligence’s societal impact during the company’s first major public appearance since achieving international prominence. Speaking at the World Internet Conference in Wuzhen on November 7, 2025, Chen painted a sobering picture of AI’s trajectory, predicting that automation could displace most human jobs within 10 to 20 years and create massive societal challenges.[reuters +3] The “Six Little Dragons” Dialogue Chen appeared alongside CEOs from five other firms—Unitree, BrainCo, Deep Robotics, ManyCore, and Game Science—collectively known as China’s “six little dragons” of AI innovation. This designation represents a new generation of Chinese tech champions emerging from Hangzhou, positioned as successors to giants like Alibaba and Tencent. The conference marked a significant moment, as DeepSeek had maintained near-total public silence since January 2025, with its only prior appearance being founder Liang Wenfeng’s February meeting with Chinese President Xi Jinping.[finance.yahoo +4] Chen’s message was deliberately paradoxical: “I’m extremely positive about the technology but I view the impact it could have on society negatively”. He outlined a two-phase disruption timeline, warning that AI could threaten job losses within 5 to 10 years as models become capable of performing tasks currently done by humans, then potentially assume most human work within 10 to 20 years. He emphasized that technology companies must act as societal “defenders” during this transition.[justsecurity +4] DeepSeek’s Meteoric Rise and Market Impact DeepSeek’s January 2025 release of its R1 reasoning model sent shockwaves through global markets. The company claimed to have developed a model matching leading U.S. competitors like OpenAI’s o1 at a fraction of the cost—reportedly just $5.6 million in computing resources. The announcement triggered historic market volatility, with Nvidia losing nearly $600 billion in market capitalization in a single day on January 27, 2025, marking the largest single-day loss in U.S. stock market history.[news.darden.virginia +4]
0
0
DeepSeek-R1 and the Emergence of Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning
This document synthesizes findings on DeepSeek-R1, a Large Language Model (LLM) whose reasoning abilities have been significantly enhanced through a novel application of pure Reinforcement Learning (RL). The core thesis is that LLMs possess substantial latent reasoning potential that can be unlocked without extensive human-annotated reasoning trajectories. By providing hard reasoning questions, a reliable verifier (reward signal), and sufficient computational resources, the model can self-evolve sophisticated problem-solving strategies. The initial model, DeepSeek-R1-Zero, was trained using RL on the DeepSeek-V3 Base model, bypassing conventional supervised fine-tuning. It achieved superior performance on verifiable tasks in mathematics, coding, and STEM fields, notably improving its score on the AIME 2024 benchmark from 15.6% to 77.9%. This process led to the emergence of advanced reasoning patterns such as self-reflection, verification, and dynamic strategy adaptation. The final model, DeepSeek-R1, builds upon this foundation through a multi-stage pipeline that integrates RL with supervised fine-tuning and rejection sampling. This approach preserves the advanced reasoning of its predecessor while aligning the model with human preferences, improving instruction-following, readability, and general capabilities. The project highlights significant limitations, including challenges in structured output, token efficiency, and the risk of "reward hacking" in domains without rule-based verifiers. The models, data samples, and distilled smaller versions have been made publicly available to advance research in AI reasoning. Core Thesis: Incentivizing Reasoning with Pure Reinforcement Learning The central argument is that the reasoning capabilities of LLMs can be substantially incentivized through a pure Reinforcement Learning framework, obviating the need for human-labelled reasoning paths. Traditional methods, such as Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting or supervised learning on human demonstrations, are effective but have key limitations:
3
0
Self-hosted DeepSeek on a lightweight, minimum install
Unsloth, an AI development team run by brothers Daniel and Michael Han, has successfully reduced the size of DeepSeek-R1 by approximately 80% using dynamic quantization techniques[1][2]. This significant reduction allows the model to run more efficiently on consumer hardware while maintaining much of its original performance. ## Key Achievements - **Size Reduction**: The original DeepSeek-R1 model, which required 720GB of storage, has been compressed to just 131GB[1][2][6]. - **Performance Retention**: Despite the drastic size reduction, the compressed model maintains 80-90% of the original model's reasoning capabilities[4]. - **Efficiency Gain**: The compressed model can achieve a throughput of 140 tokens per second and 14 tokens per second for single-user inference on dual H100s[1]. ## Dynamic Quantization Technique Unsloth's approach to compressing DeepSeek-R1 involves: 1. **Selective Quantization**: Different parts of the model are quantized at varying levels of precision[2]. 2. **MoE Layer Focus**: The Mixture of Experts (MoE) layers, which account for about 88% of the total weights, are quantized to 1.58 bits[2][5]. 3. **Precision Balance**: Critical layers like the attention mechanism and initial transformer blocks use higher precision (4-bit or 6-bit) to maintain model integrity[2][3]. ## Available Versions Unsloth has created four dynamically quantized versions of DeepSeek-R1[2]: 1. 1.58-bit version (131GB) 2. 1.73-bit version (158GB) 3. 2.22-bit version (183GB) 4. 2.51-bit version (212GB) ## Practical Implications - **Accessibility**: The compressed model can run on systems with as little as 80GB of combined VRAM and RAM[1][7]. - **Local Deployment**: Users can now run powerful AI models locally, reducing reliance on cloud services[1]. - **Cost-Efficiency**: The compression technique significantly reduces computational costs while maintaining strong performance[5]. This breakthrough in model compression demonstrates the potential for making advanced AI models more accessible and efficient, paving the way for broader adoption and application of powerful language models.
0
0
DeepSeek LLMs: Development and Team Development Timeline and Key Events
Using the technical papers published by DeepSeek, here is the timeline and dramatic personae of DeepSeek’s models/releases/innovations. The use of synthetic data, not just for training, but in an adversarial RL (reward learning) context seems as important as forward steps in attention. ***So two things in accessible language. DeepSeek improved weights/bias thru altering attention models. That’s the key in reasoning deltas. DeepSeek used synthetic data in something akin to a diffusion (think image generating AI) model. That’s the secret sauce— made necessary by resource limitations*** Pre-2024 The development of Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs) established the dominance of decoder-only Transformer architectures. These models relied on self-supervised pre-training to develop various capabilities. Techniques such as supervised fine-tuning and reward modeling were introduced to enhance model performance in alignment with user intentions and instructions. 2024 (Specific Dates Unspecified) Development of DeepSeek-Coder-V2: • A coding model focusing on long-context handling (up to 128k tokens) was developed. • Performance was assessed through pressure tests across various context lengths, demonstrating superior results. • Benchmarked against other open and closed-source models for code generation. • Mathematical reasoning abilities were evaluated on benchmarks like GSM8K, MATH, AIME 2024, and Math Odyssey. Development of DeepSeek-R1: • Reinforcement Learning (RL) techniques were integrated to enhance reasoning capabilities. • Two approaches were tested: RL on a base model and RL with a cold start. • Reward modeling, rejection sampling, and supervised fine-tuning were utilized to refine the model. • Distillation methods transferred reasoning abilities to smaller models. • Benchmarked against other LLMs in mathematical and reasoning tasks. Development of DeepSeek-V2: • A Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model was developed, focusing on efficiency and performance.
1
0
1-5 of 5

skool.com/burstiness-and-perplexity
Master AI use cases from legal & the supply chain to digital marketing & SEO. Agents, analysis, content creation--Burstiness & Perplexity from NovCog
Powered by

