
Write something
Pinned
Google’s Managed MCP and the Rise of Agent-First Infrastructure
Death of the Wrapper: Google has fundamentally altered the trajectory of AI application development with the release of managed Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers for Google Cloud Platform (GCP). By treating AI agents as first-class citizens of the cloud infrastructure—rather than external clients that need custom API wrappers—Google is betting that the future of software interaction is not human-to-API, but agent-to-endpoint. 1. The Technology: What Actually Launched? Google’s release targets four key services, with a roadmap to cover the entire GCP catalog. • BigQuery MCP: Allows agents to query datasets, understand schema, and generate SQL without hallucinating column names. It uses Google’s existing “Discovery” mechanisms but formats the output specifically for LLM context windows. • Google Maps Platform: Agents can now perform “grounding” checks—verifying real-world addresses, calculating routes, or checking business hours as a validation step in a larger workflow. • Compute Engine & GKE: Perhaps the most radical addition. Agents can now read cluster status, check pod logs, and potentially restart services. This paves the way for “Self-Healing Infrastructure” where an agent detects a 500 error and creates a replacement pod automatically. The architecture utilizes a new StreamableHTTPConnectionParams method, allowing secure, stateless connections that don’t require a persistent WebSocket, fitting better with serverless enterprise architectures. 2. The Strategic Play: Why Now? This announcement coincides with the launch of Gemini 3 and the formation of the Agentic AI Foundation. Google is executing a “pincer movement” on the market: 1. Top-Down: Releasing state-of-the-art models (Gemini 3). 2. Bottom-Up: Owning the standard (MCP) that all models use to talk to data. By making GCP the “easiest place to run agents,” Google hopes to lure developers away from AWS and Azure. If your data lives in BigQuery, and BigQuery has a native “port” for your AI agent, moving that data to Amazon Redshift (which might require building a custom tool) becomes significantly less attractive.
Pinned
poetiq:Technical Analysis for Implementation
(Live build in the Hidden State Drift Mastermind) Poetiq has achieved state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on ARC-AGI-2 with 54% accuracy at $30.57 per problem—breaking the 50% barrier for the first time and surpassing average human performance (60% is typically human baseline). This represents a 9-point improvement over the previous SOTA (45% by Gemini 3 Deep Think) at less than half the cost($77.16 → $30.57). Key Achievement Date: December 5, 2025 (officially verified by ARC Prize) 1. THE CORE INNOVATION: THE META-SYSTEM What It Is Poetiq's breakthrough is NOT a new foundation model. Instead, it's a meta-system that orchestrates existing frontier LLMs through: 1. Intelligent Multi-Agent Coordination - Multiple LLM "experts" that propose solutions, evaluate feedback, and self-audit 2. Test-Time Compute - Iterative reasoning and self-verification at inference time (not training time) 3. Adaptive Problem-Solving - Automatically selects which models, prompting strategies, and approaches (including code generation) for each specific problem 4. Cost Optimization - Achieves efficiency through intelligent early stopping and resource allocation Fundamental Design Principles "The prompt is an interface, not the intelligence" - Doesn't ask a single question; uses iterative loops - LLM generates proposed solution → receives feedback → analyzes → refines → repeats - Multi-step self-improving process builds and perfects answers incrementally Self-Auditing - System autonomously decides when it has sufficient information - Monitors its own progress and terminates when solution is satisfactory - Minimizes wasteful computation Why This Works for ARC-AGI-2 ARC-AGI-2 tests: - Abstract pattern recognition - "figure out the rule from 3 examples" - Fluid intelligence - NOT knowledge-based, requires true generalization - Spatial reasoning - Complex visual pattern relationships The core problem: Raw frontier models score below human baseline because their stochasticity makes knowledge extraction unreliable. Poetiq's meta-system systematizes knowledge extraction for complex reasoning.
3
0
Pinned
welcome to the new Burstiness and Perplexity community
Our mission is to create a true learning community where an exploration of AI, tools, agents and use cases can merge with thoughtful conversations about implications and fundamental ideas. If you are joining, please consider engaging, not just lurking.Tell us about yourself and where you are in life journey and how tech and AI intersect it. for updates on research, models, and use cases, click on the Classrooms tab and then find the Bleeding Edge Classroom
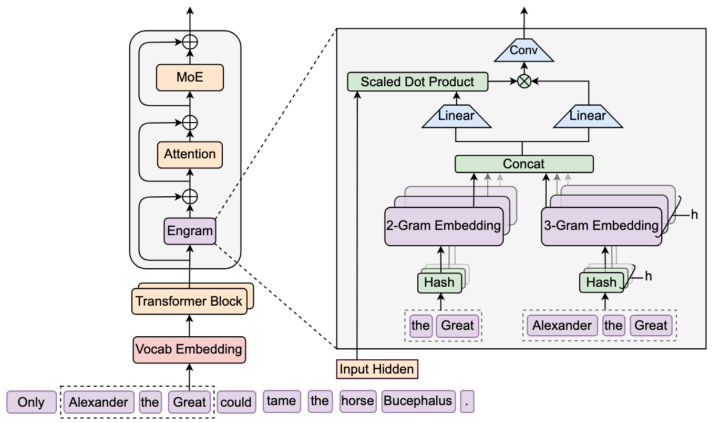
DeepSeek’s engram
I missed this one, with all my focus on context management tech and the whole stochasticity (a word I struggle to pronounce, much less type) of inference. But it is January, which means the folks at DeepSeek have made more key architecture improvements. I’ll just let them tell you (and why is their English so much better than so many native speakers). I‘ll be honest, it’s going to take me a couple days to make sense of this, but my analysis will eventually be in the Burstiness and Perplexity Skool group (bleeding edge classroom): “While Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) scales capacity via conditional computation, Transformers lack a native primitive for knowledge lookup, forcing them to inefficiently simulate retrieval through computation. To address this, we introduce conditional memory as a complementary sparsity axis, instantiated via Engram, a module that modernizes classic 𝑁-gram embedding for O(1) lookup. By formulating the Sparsity Allocation problem, we uncover a U-shaped scaling law that optimizes the trade-off between neural computation (MoE) and static memory (Engram).” #deepseek #engram #aiarchitecture #hiddenstatedriftmastermind
1
0
cool
This is how I send unlimited cold emails for free. (get unlimited clients) https://www.skool.com/cold-email-accelerator-6406/classroom/92f12090?md=30c1dbfff90e40f0ae139a903492d986
0
0
1-30 of 70

skool.com/burstiness-and-perplexity
Master AI use cases from legal & the supply chain to digital marketing & SEO. Agents, analysis, content creation--Burstiness & Perplexity from NovCog
Powered by


