
Write something
Natives
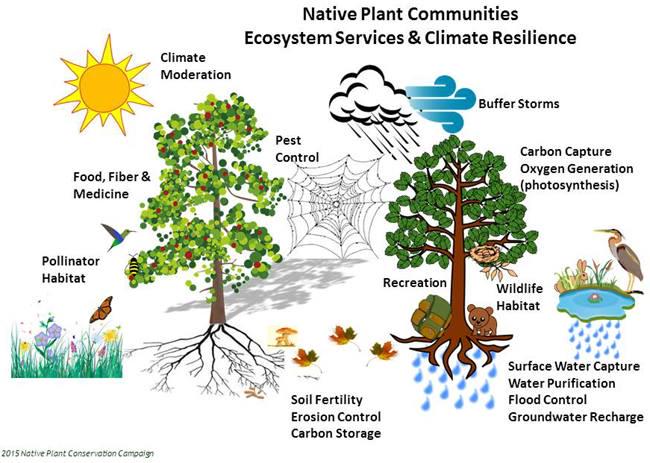
Native species are vital to ecosystems by forming the base of the food web, providing essential food and shelter for local wildlife, and supporting biodiversity. They are adapted to local conditions, which makes them more resilient and helps maintain the health of the ecosystem by improving soil health, preventing erosion, and regulating water flow. Supporting food webs and wildlife - Foundation of the food web: Native plants are the primary food source for many native insects, which in turn feed birds, fish, and other wildlife. - For example, oak trees support a vast number of insects that are critical food for birds and their young. - Habitat and shelter: Native plants provide essential shelter, nesting sites, and breeding grounds for local animals like birds, mammals, and insects. - Pollinator support: They provide essential nectar and pollen for native pollinators like bees and butterflies, which are crucial for the reproduction of many plant species, including crops. Maintaining ecosystem health - Soil health: Native plants, with their deep root systems, help stabilize soil and prevent erosion. They also improve soil structure and increase organic matter, which enhances nutrient cycling and water absorption. - Water conservation: Because they are adapted to local rainfall patterns, native plants often require less water and are more drought-tolerant, helping to conserve water resources. - Flood and stormwater control: The dense growth and deep roots of native plant communities are effective at slowing surface water flows, which helps prevent flooding and filter runoff. Building resilience - Biodiversity: By supporting a wide range of native species, they contribute to a healthy and diverse ecosystem that is more resilient to environmental changes, diseases, and invasive species. - Pest resistance: Native plants have often evolved alongside local pests, which can give them natural defenses and reduce the need for chemical pesticides. - Climate regulation: They help combat climate change by sequestering carbon, and their ability to manage water and soil is vital for mitigating the impacts of climate change.
1-1 of 1

