Activity
Mon
Wed
Fri
Sun
Apr
May
Jun
Jul
Aug
Sep
Oct
Nov
Dec
Jan
Feb
Mar
What is this?
Less
More
Memberships
Onyx Elite Performance
138 members • $147/month
6 contributions to Onyx Elite Performance
Motivational Quote 💭
Meditations: Book 3 “We must take into our reckoning not only that life is expended day by day and the remaining balance diminishes, but also this further consideration: if we live longer, there is no guarantee that our mind will likewise retain that power to comprehend and study the world which contributes to our experience of things divine and human. If dementia sets in, there will be no failure of such faculties as breathing, feeding, imagination, desire: before these go, the earlier extinction is of one's proper use of oneself, one's accurate assessment of the gradations of duty, one's ability to analyse impressions, one's understanding of whether the time has come to leave this life - these and all other matters which wholly depend on trained calculation. So we must have a sense of urgency, not only for the ever closer approach of death, but also because our comprehension of the world and our ability to pay proper attention will fade before we do.” -Marcus Aurelius This passage in the book made me contemplate on the amount of time I wasted and let slip me by not doing “what I was supposed to be doing”. It also motivates me to live by the saying “momento mori” or “remember you must die”, which lights a fire in me to take action. In times of regret I think of my favourite quote… “I am not what happened to me, I am what I choose to become" -Carl Jung

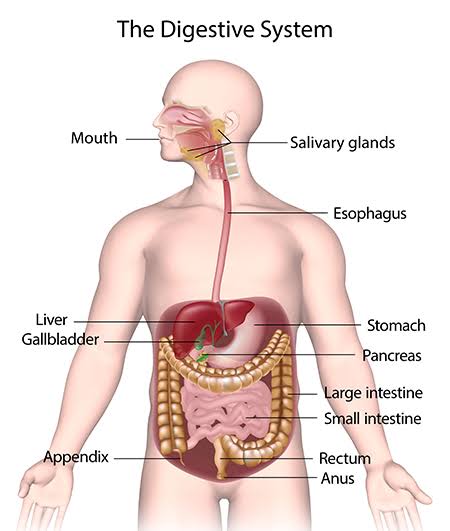
Nutritional Tips for Optimal Digestion
“We are what we eat” but we are also “how we eat”, this is often a neglected aspect of diet and nutrition. Here are some tips on how to improve your digestion through scientifically proven protocols: - 20 minutes prior to when you plan to eat, drink 1-2 glasses of water: This will allow your body to produce and maintain the correct moister levels in your stomach lining to aid food passing through efficiently. - Avoid drinking water during your meal, if needed only small sips should be taken to get food down: This is because when we drink water during the eating process it creates too much liquid in the stomach leading to a dilution of stomach acid which is in charge of breaking down the food entering your stomach. - Reduce and preferably eliminate excess noise/distractions while eating where possible: Consuming any media or news related topics directly spike cortisol (stress), which puts us in sympathetic nervous system mode (fight/flight). Loud noises create this same effect and that state is the antithesis of parasympathetic nervous system (rest/digest) which is optimal for times we are eating. “Eat your liquids and drink your solids” this rule outlines the importance of chewing food 30-100 times before swallowing as this gives our body the best chance to absorb nutrients to be converted into fuel (energy).
5
0
Myers Briggs Personality Test🪞
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) The MBTI helps people understand their personality preferences, which can be helpful in understanding how they interact with the world and others. It's a tool for self-discovery and improving interpersonal relationships. Also, as coaches in this community, it gives us an extra insight into how you view yourself so we can better understand you as well. - Four Dichotomies: The test uses four pairs of opposing preferences to categorize individuals: Extraversion (E) vs. Introversion (I): How individuals focus their energy – outward toward the external world or inward toward their inner world. Sensing (S) vs. Intuition (N): How individuals perceive information – directly through their senses or through patterns and possibilities. Thinking (T) vs. Feeling (F): How individuals make decisions – based on logic and analysis or on values and emotions. Judging (J) vs. Perceiving (P):How individuals prefer to live their outer life – structured and organized or flexible and adaptable. - 16 Personality Types: By combining preferences from each of the four dichotomies, the MBTI results in 16 distinct personality types. Here's a breakdown of the 16 personality types: Analysts: - INTJ (The Architect): Strategic, independent, and insightful. - INTP (The Logician): Innovative, curious, and logical. - ENTJ (The Commander): Bold, decisive, and natural leaders. - ENTP (The Debater): Intellectually curious, resourceful, and argumentative. Diplomats: - INFJ (The Advocate): Idealistic, insightful, and inspiring. - INFP (The Mediator): Creative, compassionate, and value-driven. - ENFJ (The Protagonist):Charismatic, empathetic, and inspiring. - ENFP (The Campaigner):Enthusiastic, imaginative, and outgoing. Sentinels: - ISTJ (The Logistician): Practical, responsible, and detail-oriented.
6
0

Level 2 - Welcome 🫶
A warm welcome to our upgraded Level 2 members. I'm excited to have you all an integral part of this offering and Community. All specific Level 2 group communication moving forward will be posted in a private WhatsApp discussion group. (link will be sent to your inbox) I'm looking forward to creating a space for you to Immerse, Adapt and Evolve towards optimum health, performance, connection, community and longevity! Please follow the prompts below to assist in navigating through our foundational starting point in Level 2. Here we set the tone and receive insights to you and your current state of health by actioning a myriad of different screening protocols. Step 1 : Click on the Onyx Elite Questionnaire link and allocate some time and space to fill out in depth. You can find questionnaire link under 'resources tab'. Step 2 : Click on the i:screen Health Screening tab. An intelligent health screening solution that tracks key biomarkers in your blood before they become an issue. We provide online access to the tools, insight and medical expertise to help you make better health decisions, avoid preventable illness and work towards optimum health and wellbeing. https://www.i-screen.com.au/?referral=onyx Click (https://www.i-screen.com.au/?referral=onyx%26%2365532%3BClick)onon) link above for full blood profile. Click on ‘Well Man Check’ or ‘Well Woman Check’ respectively. Once you receive your results, please email them to : j.onyxelite@gmail.com Step 3 : Click on the Functional Health Assessment tab and read the first page, then click on google sheets link and save to your computer to record all your testing results. The 38 tool protocol can be found under 'resources tab', named Function Health Assessment. All instructions and information on how to undertake the assessment is detailed within this folder. Once you have completed tests, taken photos and recorded all data on the google sheet link, please email to : j.onyxelite@gmail.com

BOLT Score Test
A simple, objective measure of breathlessness and of chemosensitivity to carbon dioxide. The breath is held after a normal exhalation until the first definite desire to breathe. The time of the breath hold is counted in seconds. This gives you your BOLT score. A BOLT score lower than 25 seconds indicates a stronger ventilatory response to CO2 and dysfunctional breathing. During the normal respiratory cycle, carbon dioxide accumulates in the blood. When the body is overly sensitive to the build-up of carbon dioxide, breathing becomes harder during rest, physical exercise and in sleep apnea patients. This is because CO2 plays an important role in respiratory biochemistry, providing the primary stimulus to breathe and facilitating the release of oxygen from the red blood cells to the tissues and organs. To obtain an accurate measurement, it’s best to rest for ten minutes before measuring your BOLT score. Read the instructions carefully first and have a timer on hand. You can measure your BOLT now: Take a normal breath in through your nose and allow a normal breath out through your nose. Hold your nose with your fingers to prevent air from entering your lungs. Time the number of seconds until you feel the first definite desire to breathe, or the first stresses of your body urging you to breathe. These sensations may include the need to swallow or a constriction of the airways. You may also feel the first involuntary contractions of your breathing muscles in your abdomen or throat as the body gives the message to resume breathing. Release your nose, stop the timer, and breathe in through your nose. Record your BOLT Score and post in comments 🌬️

1-6 of 6
Active 184d ago
Joined Apr 18, 2025
INTJ
Powered by


