
Write something
🧠 Mind Mapping Magic: Unlock Creativity, Memory, and Fun!
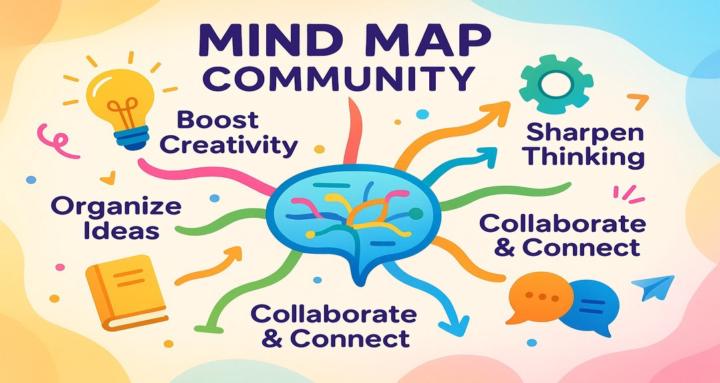
Absolutely! Here’s your post about mind maps, enhanced with emojis for attention and a fun vibe: 🧠 What Is a Mind Map? A mind map is a visual tool for organizing information, ideas, or concepts around a central topic. It uses branches, colors, and images to show connections, making complex information easier to understand and recall. Start with a main idea in the center, then branch out with related topics. 🌳✨ 🔬 Science-Backed Benefits of Mind Mapping - Boosts Creativity 🎨: - Enhances Memory & Retention 🧩: - Improves Organization & Clarity 🗂️: - Facilitates Learning 📚: - Promotes Collaboration 🤝: 💡 Popular Use Cases for Mind Maps 1. Brainstorming – Capture creative ideas with freedom! 🧠💥 2. Note-Taking – Summarize and remember key points easily. ✍️📝 3. Project Planning – Visualize projects and deadlines at a glance. 📅🚀 4. Studying – Organize study topics for better exam results. 🎓📖 5. Decision-Making – Compare options side by side. ⚖️🤔 6. Goal Setting – Map out your goals and steps. 🥅🗺️ 7. Problem Solving – Reveal connections and solutions visually. 🔍🛠️ 🧩 Why Mind Maps Work Mind maps align with how our brains naturally process information—visually and associatively. By engaging both visual and verbal memory, mind mapping makes learning, recalling, and problem-solving more effective. Science shows mind maps help us learn faster, think more creatively, and collaborate better. 🚀 Ready to Try Mind Mapping? Grab some paper or try a digital tool! Place your main idea in the center and let your ideas branch out naturally. Add colors, symbols, and doodles—your brain will thank you! 🖍️🌈 How do you use mind maps? Share your favorite tips or stories below! 💬👇 📚 References - Al-Jarf, R. (2009). Thinking Skills and Creativity, 4(1), 60-67. - Farrand, P., Hussain, F., & Hennessy, E. (2002). Medical Education, 36(5), 426-431. - Wickramasinghe, D. P., et al. (2007). Medical Education Online, 12(1), 2-7.
1-1 of 1
powered by
skool.com/mind-map-5659
🌍 A community of Makers shaping the future with passion, vision, and action. Let’s build a better world — together. 🚀
Suggested communities
Powered by
