Activity
Mon
Wed
Fri
Sun
Feb
Mar
Apr
May
Jun
Jul
Aug
Sep
Oct
Nov
Dec
What is this?
Less
More
Owned by Rob
Break free from addictions alongside like-minded individuals. Gain essential tools and strategies building healthier habits, and reclaim your life
Memberships
2 contributions to FREEDOM -Quit Your Addictions
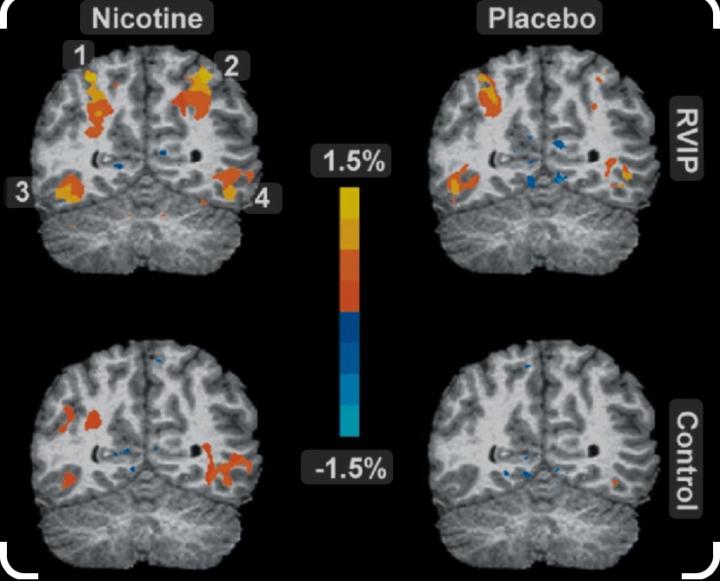
How Smoking Changes Your Brain
The impact of smoking on mental health and behavior have intensified. While many view smoking as a personal choice or a stress-relief mechanism, emerging research suggests it can significantly alter brain function and have profound effects on overall well-being. Neurological Changes Dopamine Release: Smoking nicotine triggers the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. This immediate boost in dopamine reinforces the behavior, leading to a cycle of dependence. Over time, the brain becomes desensitized, requiring higher doses of nicotine to achieve the same pleasurable effects, which can escalate smoking behavior. Psychological Effects Increased Anxiety and Depression: Research has linked smoking with heightened levels of anxiety and depression. Although many individuals initially smoke to alleviate stress, the addictive nature of nicotine can exacerbate mental health issues over time. This paradox often stems from withdrawal symptoms and the negative health consequences of smoking, creating a cycle that is difficult to break. Understanding these impacts is crucial for promoting healthier choices and supporting those seeking to quit
0
0
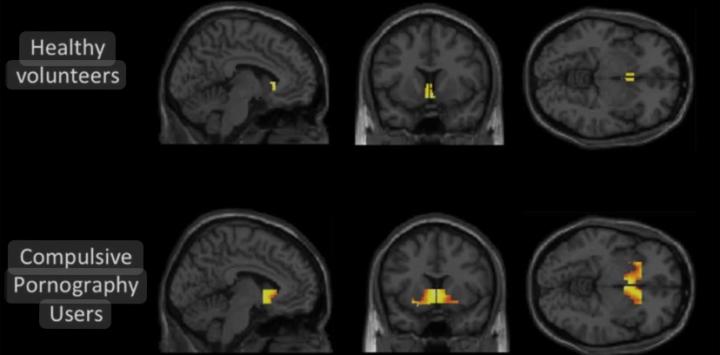
How Porn Changes Your Brain
In recent years, discussions around the impact of pornography on mental health and behaviour have gained traction. While many view porn as a harmless form of entertainment, emerging research suggests it can significantly alter brain function and affect relationships. Neurological Changes: Dopamine Release: Watching porn triggers a massive release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. Over time, this can lead to desensitization, meaning individuals may require more extreme stimuli to achieve the same level of satisfaction. Psychological Effects: Increased Anxiety and Depression: Research has linked high levels of porn consumption with increased symptoms of anxiety and depression. This may stem from the disconnect between fantasy and reality, or from guilt and shame associated with porn use.
0
0
1-2 of 2
@rob-herts-1117
Creator Of Freedom - Quit porn for good skool community/course
Active 132d ago
Joined Oct 1, 2024
Powered by

