Activity
Mon
Wed
Fri
Sun
Mar
Apr
May
Jun
Jul
Aug
Sep
Oct
Nov
Dec
Jan
What is this?
Less
More
Memberships
QA Automation Accelerator
487 members • Free
4 contributions to QA Automation Accelerator
Web DOM: A Complete Guide for QA Automation Engineers
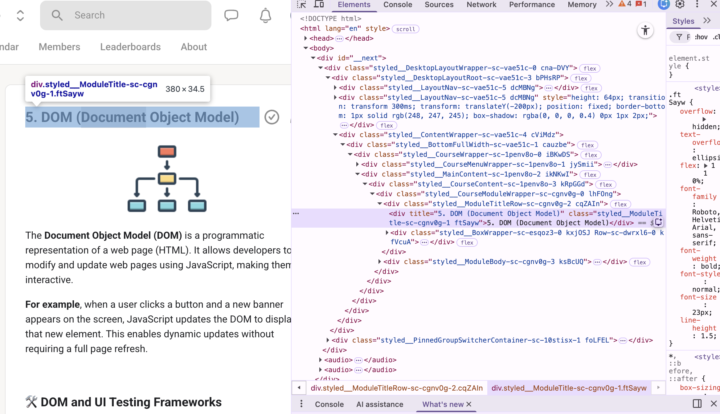
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐃𝐨𝐜𝐮𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭 𝐎𝐛𝐣𝐞𝐜𝐭 𝐌𝐨𝐝𝐞𝐥 (𝐃𝐎𝐌)? The Document Object Model (DOM) is a programmatic representation of a web page (HTML). It allows developers to modify and update web pages using JavaScript, making them interactive. This is what enables users to: - Click buttons - Fill forms - See dynamic content appear and disappear ℹ️ When a user interacts with a website, JavaScript updates the DOM behind the scenes to reflect those changes without refreshing the whole page. 𝐒𝐢𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞 𝐞𝐱𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞: When a user clicks "Add to Cart" on an e-commerce site, the cart icon updates and a message appears. That's JavaScript updating the DOM to show those changes instantly. 𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐭𝐨 𝐕𝐢𝐞𝐰 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐈𝐧𝐬𝐩𝐞𝐜𝐭 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐃𝐎𝐌 Opening the DOM Inspector 1. Right-click anywhere on a webpage 2. Select "Inspect" 3. Look at the "Elements" tab content 𝐔𝐧𝐝𝐞𝐫𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐃𝐎𝐌 𝐒𝐭𝐫𝐮𝐜𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐞 You'll see all the HTML elements organized in a tree structure: - Elements can be expanded or collapsed to view their contents - Each element has parent, child, and sibling relationships - The structure reflects the nesting of HTML tags ℹ️ When you right-click and inspect a specific element, the Elements tab automatically highlights that exact element in the tree. ──────────────────────────────────────── 🟢 𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐃𝐎𝐌 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐖𝐡𝐲 𝐒𝐡𝐨𝐮𝐥𝐝 𝐐𝐀 𝐄𝐧𝐠𝐢𝐧𝐞𝐞𝐫𝐬 𝐂𝐚𝐫𝐞? The Document Object Model (𝐃𝐎𝐌) is the bridge between a test automation code and the web pages you're testing. Testing frameworks like Playwright rely on DOM manipulation to execute automated tests: - Element Location: Frameworks use CSS selectors and XPath to find elements in the DOM - Action Simulation: Clicks, text input, and navigation all happen through DOM interaction ──────────────────────────────────────── 🟠 𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐐𝐀 𝐀𝐮𝐭𝐨𝐦𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐖𝐨𝐫𝐤𝐟𝐥𝐨𝐰: 𝐒𝐭𝐞𝐩 𝟏: Identify Target Elements Open Developer Tools (F12) and inspect the elements you need to interact with: ⟩ Find unique identifiers (IDs, classes, attributes) ⟩ Identify selectors that won't break easily (avoid dynamic IDs or complex nested paths)
API testing... It's important
As I grow deeper into my automation role. I've realized the importance of API testing, understanding it and how to use it in automation testing, even if you're testing UI. Thoughts?
Cypress World is limited
Cypress, has various limitations, my question is has any one ever mixed Cypress with Selenium or injected Selenium in certain sections where Cypress can't test?
Manual QA Goodbye!
I went from Manual QA to Automation. It's a huge payoff.
1-4 of 4


