Activity
Mon
Wed
Fri
Sun
Jan
Feb
Mar
Apr
May
Jun
Jul
Aug
Sep
Oct
Nov
What is this?
Less
More
Memberships
AI Workshop Lite
12.5k members • Free
AI Automation Society
202.6k members • Free
GTM Academy AI (FREE)
55 members • Free
6 contributions to GTM Academy AI (FREE)
We're so excited to have you here!
Hey everyone! Welcome to GTM Academy AI. We’re so excited to have you here. Quick update on what’s coming up: we’re planning some tutorials and Q&A sessions to help you get the most out of the community and tools. And when I say we, there are three Co-Founders behind this: @Evelyn Lopez Delon , @Ken Thomas, and myself. Plus, you’ll have support from all of us and the wider community as we grow together. We’ll also be rolling out monthly Collaboration & Connection sessions soon. These will be awesome opportunities to learn from each other, share insights, and build strong connections. To make the most of those sessions, it’d be great to get to know each other a bit first. So please comment below sharing: - A bit about you: your role, location - Why you joined GTM Academy AI - One thing you’re excited to learn or achieve here - Something fun or random about you No pressure—just be yourself! This helps everyone get a feel for who you are and starts the connections that’ll make this community thrive. The right intro can spark unexpected opportunities. You never know what conversation or opportunity that one small post could unlock. Once you post, jump around and welcome a few others too. We’re building something special, and it starts with you. Can’t wait to see your intros! -Adam
1 like • Oct 12
I dont think it would work out well for a human to grapple with a robot. There is such a subtle difference between tension in a jointlock and a break/snap. Its hard enough to trust good training partners to avoid injuries, let alone something with hydraulics or actuators! I have always been an early adopter of technology but for some things, i have gone back to manual control since i like to be in control of certain aspects, and others i do use automation. The more we offload the more reliant we become. Ill make a post separate that come to mind from this concept.
2 likes • Oct 15
@Adam Lopez Delon I saw that one a while back, something like that is more just a dummy with sensors and is only really good for beginners learning the basic techniques and how to apply them, eg, tension in an armbar or pressure for a choke, the majority of training after that initial period is learning not only how to perform a technique against a resisting opponent actively defending, but the 'chess' like strategy. if they do this move, you react and do that, then they switch to this and you counter with that etc.. That aside, my local gym has a great group of people. Half the benefits of jiu-jitsu is the social environment and training with other like minded people :)
Cognitive Offloading
Cognitive offloading refers to the practice of using external tools, technology, or resources to reduce the mental burden of storing, processing, or recalling information. Examples include using calendars, note-taking apps, calculators, gps or even writing things down. Below are some pros and cons of cognitive offloading, presented concisely: **Pros** 1. **Enhanced Efficiency**: Offloading tasks like calculations or memorization to tools (e.g., calculators, apps) frees up mental resources, allowing focus on higher-order thinking or creativity. 2. **Improved Accuracy**: Tools like spell-checkers or data storage systems reduce human error in tasks like writing or recalling facts. 3. **Increased Productivity**: By outsourcing routine cognitive tasks (e.g., reminders in apps), you can manage time better and handle more complex projects. 4. **Accessibility**: External tools make information available anytime, anywhere, unlike memory, which can be unreliable. 5. **Stress Reduction**: Relying on tools for reminders or organization reduces mental clutter and anxiety about forgetting important details. ** Cons ** 1. **Over-Reliance on Technology**: Depending heavily on tools can weaken natural cognitive abilities, like memory or problem-solving, over time. 2. **Potential for Errors**: Tools can malfunction, be misused, or provide incorrect outputs (e.g., GPS errors or software bugs), leading to mistakes. 3. **Loss of Skill Development**: Constantly offloading tasks like mental math or navigation may hinder learning or skill retention. 4. **Privacy Concerns**: Storing personal information in digital tools (e.g., note apps or cloud services) risks data breaches or unauthorized access. 5. **Disconnection from Intuition**: Relying on external systems may reduce trust in one’s own judgment or instincts for decision-making. *** Summary *** Cognitive offloading can boost efficiency and reduce mental strain, but it risks over-dependence, skill erosion, and privacy issues. Balancing tool use with cognitive practice is key to maximizing benefits while minimizing drawbacks.
LM Arena - AI Comparison
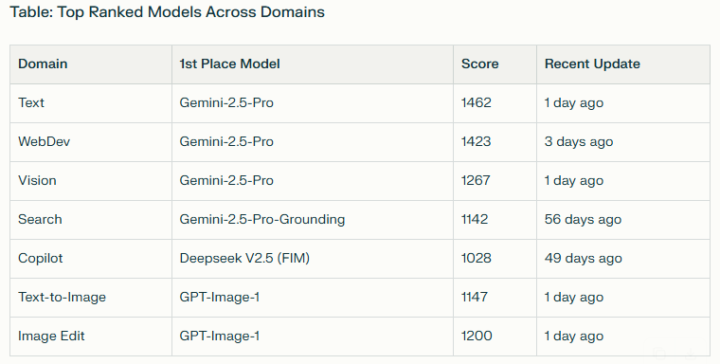
https://lmarena.ai/leaderboard/ The leaderboard at lmarena.ai/leaderboard offers a comparative overview of leading AI models across several domains, including text generation, web development, vision (image tasks), search, copilot/code, text-to-image, and image editing. Models are ranked based on their performance scores, with dedicated tabs for deeper domain-specific insights. -------------------------------- Use it to decide which LLM tool best suits your application. Good to see some Open Source models right up there with the leading closed models, eg. Qwen3, deepseek, kimi, glm and mistral
Open Source AI Models
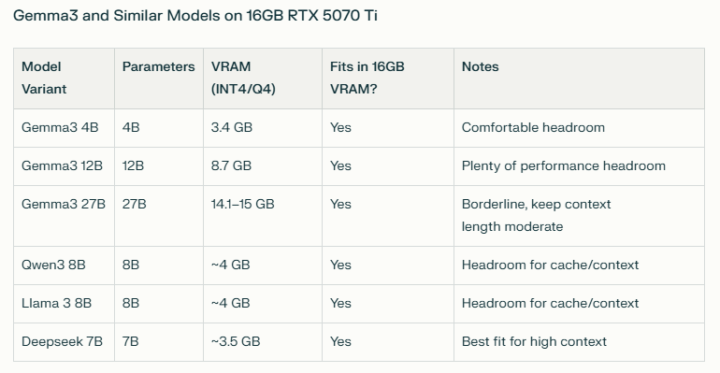
https://huggingface.co/ Hugging Face (huggingface.co) is a leading AI platform and open-source community where developers, researchers, and organizations collaborate to create, share, and deploy machine learning models, datasets, and applications, especially in the field of natural language processing (NLP). The easiest ways to run open source AI models locally are with user-friendly tools like https://ollama.com/ and https://lmstudio.ai/, which remove the need for complex setup or coding skills and work well on Windows, Mac, and Linux systems. Just keep in mind that the size (GB) of your AI model should ideally fit fully within your GPU VRAM, otherwise it will offload to the CPU and drastically reduce the speed (tokens per second).
1 like • Sep 29
I also run a local home server with some open source models and find gemma3, qwen3, deepseek the best around 8B-14B parameters. gpt-oss:20B (13GB) is Open AI's open source model for use on consumer hardware and works well too. IBM's granite3.3:8B (4.9GB) and NVIDIA's nemotron-mini:4B (2.7GB) are great lightweight models which should fit on average GPU's.
AI Powered Browser
https://www.perplexity.ai/comet Comet Browser is a new AI-powered web browser developed by Perplexity, designed to enhance productivity and user experience by integrating advanced artificial intelligence tools directly into the browsing environment. Built on Chromium, Comet supports familiar features like Chrome extensions and bookmarks, making the transition seamless for most users. Comet is positioned as a next-generation browser that transforms passive web surfing into an interactive, AI-driven workflow, aiming to set a new standard for intelligent, agentic browsing. ----------------------------------------------------------- I recommend trying it out. Its quickly become my preferred browser so I don't need to have multiple tabs open to use multiple AI tools.
1-6 of 6
Active 19d ago
Joined Sep 25, 2025
Powered by

